Explore how cancer progresses in older people, from risk factors to treatment innovations, focusing on quality of life.
He cancer, one of the most feared and complex diseases of the 21st century presents particular characteristics in older people.
This article seeks to provide a deep understanding of how cancer progresses in this age group, addressing everything from diagnosis to treatment and the particularities that differentiate it in the elderly.
Risk factors and types of cancer prevalent in older people
Specific risk factors in the elderly
In older people, Cancer risk factors are unique and multifaceted. On the one hand, the cumulative exposure to carcinogens throughout life, such as smoking or exposure to certain chemicals, increases the risk.
Furthermore, biological changes associated with aging, such as alteration in metabolism and lower efficiency in DNA repair contribute significantly.
Another key aspect is the immunosenescence, the progressive decline of the immune system, which reduces the body’s ability to fight cancer cells. The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) emphasizes the importance of considering these factors to better understand how cancer progresses in older people.
Most common types of cancer
In the older population, certain types of cancer are more common. The prostate cancer for example, is predominantly a disease of older men, with risk increasing significantly with age.
Likewise, the breast cancer In older women it often presents different characteristics compared to younger patients.
Cancers of colon and lung They also show a high prevalence in this age group, with particular aspects in their development and progression. According to the International Cancer Research Center (IARC), these types of cancer require screening and treatment strategies tailored to older people.
Detection and diagnosis in the elderly
Challenges in early detection
The early detection It is crucial to improve cancer treatment outcomes. However, in older people, there are significant barriers.
The decreased mobility and sensory problems may prevent them from getting regular checkups. In addition, there is a tendency to attribute certain symptoms to “age problems”, which can delay diagnosis.
According to studies published in the Journal of Geriatric Oncology the promotion of adapted screening programs to the needs and limitations of older people could improve early detection in this group.
Differences in clinical presentation
Cancer in older people often manifests differently compared to younger patients. The symptoms can be more subtle or atypical leading to late diagnoses.
This variability in symptoms, together with the presence of other chronic diseases, complicates clinical interpretation and, consequently, how cancer progresses in older people.
The International Federation of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) recommends that clinicians be particularly attentive to these differences in clinical presentation to avoid delays in diagnosis.
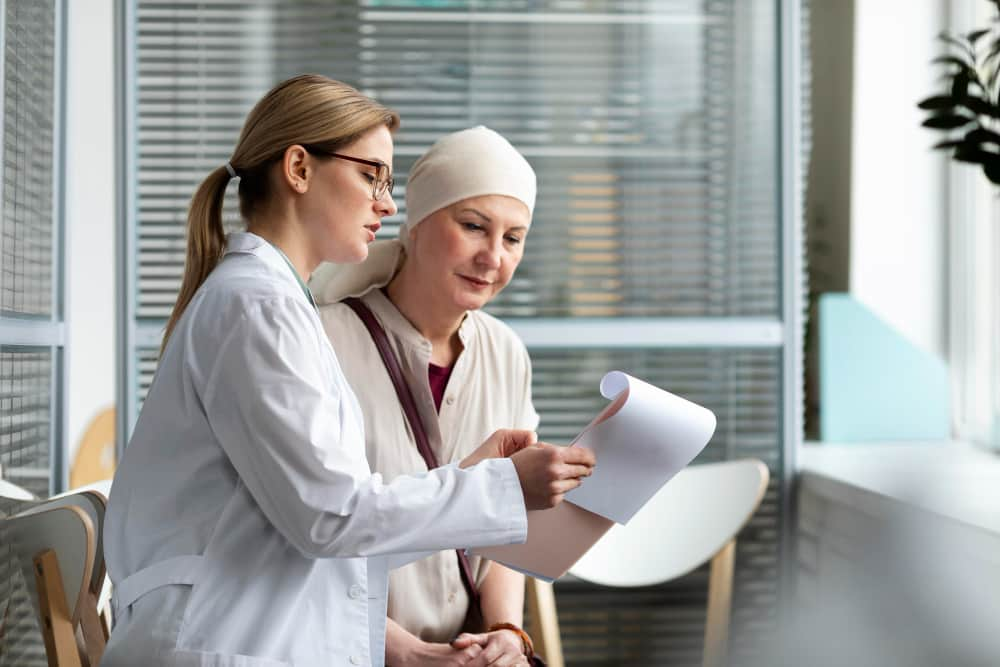
Cancer treatment in older people
Challenges in treatment selection
Selecting the most appropriate treatment in older people with cancer is a challenge. One must take into account not only the type and stage of the cancer, but also the general health status, existing comorbidities and tolerance to possible side effects.
Standard treatment regimens may need adjustments to minimize risks and maximize effectiveness. According to him National Cancer Institute (NCI)Understanding and managing these challenges is essential to improving how cancer progresses in older people.
Customized approaches
Personalized treatments are crucial in geriatric oncology. Consider the fragility and specific conditions of each patient allows therapies to be adapted to balance effectiveness with quality of life.
This individualized approach is essential to effectively manage how cancer progresses in older people offering treatments that best align with each patient’s needs and limits.
Quality of life and palliative care
Maintaining quality of life
Maintaining quality of life is a primary goal in the treatment of older people with cancer. This includes not only the effective pain management and other physical symptoms, but also the emotional and social support.
Adapting living environments and including support services can play a crucial role in the overall well-being of these patients.
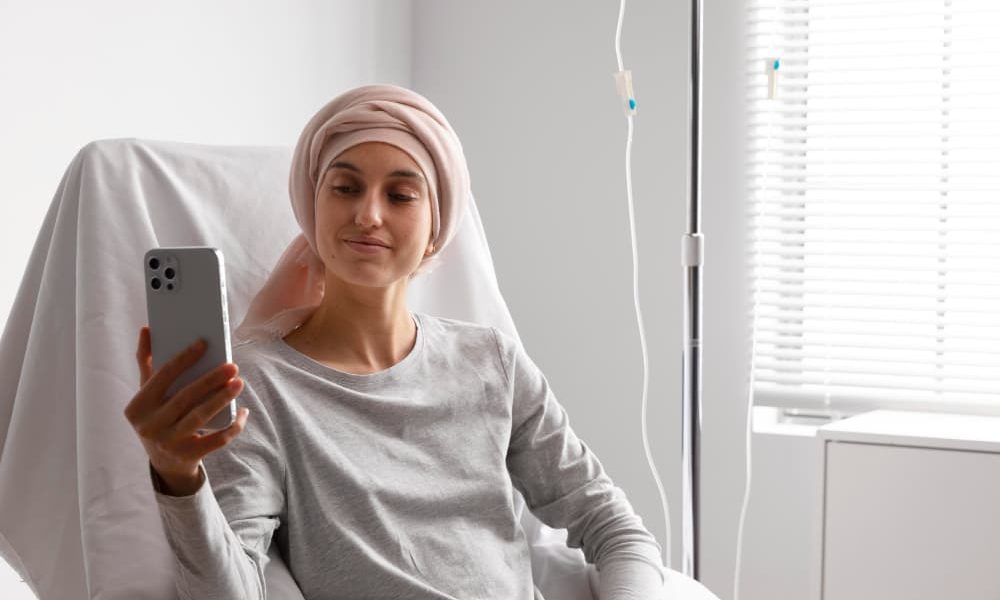
Importance of palliative care
Palliative care is essential, especially for those with advanced cancer. This care focuses on relieve pain and other symptoms thus improving the quality of life.
The World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizes that palliative care should be an integral part of cancer treatment in older people, considering both physical and emotional needs.
Innovations and advances in treatment
The development of new therapies and technologies is revolutionizing cancer treatment in older people. These advances promise more effective and less invasive treatments, adapted to the needs and abilities of this age group.
Targeted therapies and precision medicine
Targeted therapies and precision medicine represent a major advance in the treatment of cancer in older people.
These approaches use information about the cancer and the patient’s genetics to develop more specific and less toxic treatments.
These therapies are designed to specifically attack cancer cells, minimizing damage to normal cells and improving how cancer progresses in older people.
Advances in immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, which strengthens or restores the ability of the immune system to fight cancer, has shown promising results, particularly in types of cancer that have traditionally been difficult to treat.
These treatments may be especially beneficial for older people, offering less invasive options with potentially fewer side effects.
Towards a more hopeful future
The progression of cancer in older people is a complex network of biological, social and medical factors. The key to improving results lies in a personalized approach that considers the particularities of each patient.
With advances in early detection, personalized treatments and palliative care, the future looks more hopeful for older people facing this disease.
The fight against cancer in the elderly is an ongoing challenge, but with research and proper care, It is a challenge that we are better prepared to face every day.